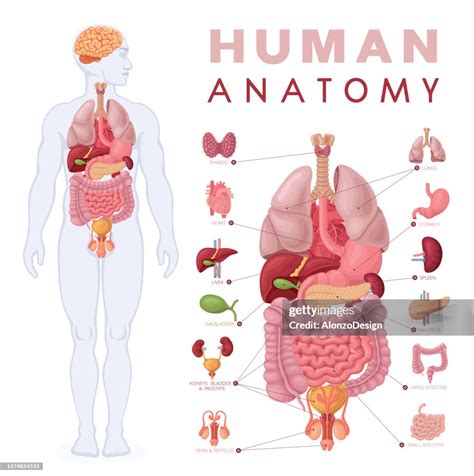
Human Bones: Your Body’s Incredible Foundation\n\nAlright guys, let’s dive deep into something truly
amazing
and often taken for granted: our very own
human bones
. These aren’t just rigid structures holding us up; they’re dynamic, living tissues that form the incredible foundation of our bodies. From the tiniest bones in your ears that help you hear the world’s sweet melodies, to the massive femur in your leg that supports your entire weight,
human bones
play a pivotal role in almost everything we do. Think about it: every step you take, every time you reach for your coffee, every protective embrace – it’s all thanks to your skeletal system. This isn’t just biology class; this is about understanding the unsung heroes working tirelessly inside you, day in and day out. Our goal here isn’t just to list facts, but to genuinely appreciate the complex engineering and biological marvel that is our skeleton. We’re going to explore what these bones are made of, their surprising functions beyond just support, and how we can keep them strong and healthy for a lifetime. So, buckle up, because we’re about to uncover the
secrets of your body’s most resilient framework
. We’ll chat about the different types of bones, how they work together to facilitate movement, and even their crucial role in producing blood cells and storing essential minerals. It’s a journey into your inner self, highlighting why maintaining good
bone health
is absolutely non-negotiable for a vibrant and active life. Get ready to have your mind blown by the sheer ingenuity of your own anatomy, and how these fundamental components empower your entire existence. This comprehensive guide aims to arm you with all the knowledge you need to appreciate and care for these vital parts of your
skeletal system
. Prepare to be amazed by the intricate dance of cells and minerals that build your sturdy internal framework. By the end of this article, you’ll have a newfound respect for the bones that quite literally hold you together, making you realize they are far more than just “tulang belulang” – they are the very essence of your physical being. Let’s get started on this exciting exploration of
human bones
and their incredible story!\n\n## What Are Human Bones, Anyway? The Basics of Your Skeletal System\n\nSo, what exactly are these
human bones
that form our
skeletal system
? At their core, bones are complex, living organs, not just inert structures. They’re primarily composed of a matrix of collagen fibers (a protein) reinforced with calcium phosphate, a mineral that gives bones their characteristic hardness and rigidity. This unique composition makes bones strong yet somewhat flexible, capable of withstanding significant stress and impact. We’ve got two main types of bone tissue, guys:
compact bone
and
spongy bone
. The
compact bone
, also known as cortical bone, is the dense, hard outer layer that accounts for about 80% of the skeletal mass. This stuff is super strong and forms the shaft of long bones and the outer shell of all bones. It provides protection, support, and helps in storing calcium. Then, deeper inside, we find
spongy bone
, or cancellous bone. This tissue is less dense, with a porous, honeycomb-like structure. It’s found at the ends of long bones, in vertebrae, and in the pelvis. While it might look delicate,
spongy bone
is incredibly important because its open structure allows it to contain
bone marrow
, where our amazing body produces red and white blood cells, and platelets. This internal architecture also helps the bone withstand stress from multiple directions and lightens the overall weight of the skeleton.
Bone composition
is a fascinating balance of organic and inorganic materials, giving them both tensile strength (resistance to being pulled apart) and compressional strength (resistance to being squeezed). Without this intricate balance, our bones would either be too brittle and shatter easily, or too flexible and unable to provide stable support. Beyond just the tissue, each bone is wrapped in a protective membrane called the
periosteum
, which contains blood vessels and nerves, and plays a crucial role in bone repair and growth. The
skeletal system
isn’t static; it’s constantly undergoing a process called remodeling, where old bone tissue is broken down by osteoclasts and new bone tissue is built up by osteoblasts. This continuous turnover ensures our bones remain strong, adapt to stresses, and repair minor damages, preventing the accumulation of old, brittle bone. This dynamic nature is what makes our
human bones
so resilient and vital to our overall health. Understanding this basic structure and continuous activity is key to appreciating just how incredible your internal framework truly is. It’s a testament to evolutionary design, ensuring our bodies have a robust and adaptable support system. So, next time you think of bones, remember they are far more than just inert scaffolding; they are vibrant, living components of your
body’s foundation
.\n\n## More Than Just Structure: The Amazing Functions of Bones\n\nWhen we think about
human bones
, the first thing that usually comes to mind is support. And yes, providing a rigid framework for the body is a primary
function of bones
, preventing us from being a floppy mess, but that’s just the tip of the iceberg, guys! Our
skeletal system
performs an astounding array of vital roles that are crucial for our survival and well-being. Firstly, there’s
protection
. Imagine trying to walk around without a hard casing protecting your brain – nope! Your skull is a tough helmet for your most vital organ, and your rib cage acts like a sturdy shield for your heart, lungs, and other delicate internal organs. These protective capabilities are absolutely essential, minimizing damage from external forces and ensuring our most vulnerable parts are kept safe. Secondly,
movement
is entirely dependent on our bones. While bones themselves don’t move, they act as levers. Muscles, attached to bones via tendons, contract and pull on these levers, allowing us to walk, run, jump, lift, and perform countless other actions. Without the precise articulation of
human bones
at joints, coordinated movement would be impossible. It’s a masterful collaboration between the muscular and
skeletal system
that enables our incredible agility. But wait, there’s more! Bones are also critical for
mineral storage
, particularly calcium and phosphorus. These minerals are not just structural components; they are vital for nerve function, muscle contraction, blood clotting, and energy metabolism. Bones act as a massive reservoir, releasing these minerals into the bloodstream when levels drop and absorbing them when levels are high. This delicate balance, maintained by your
bone health
, is essential for numerous physiological processes throughout the body. Perhaps one of the most surprising and vital functions is
blood cell production
. Tucked away inside the spongy bone, especially in larger bones like the pelvis, sternum, and vertebrae, is the
red bone marrow
. This incredible tissue is the factory responsible for producing all our red blood cells (which carry oxygen), most white blood cells (our immune system’s soldiers), and platelets (for blood clotting). Without healthy bone marrow, our entire circulatory and immune systems would fail. This process, called hematopoiesis, underscores the dynamic and life-sustaining role of our bones beyond mere structural support. Lastly, recent research has even highlighted an
endocrine function
of bones. They produce hormones, such as osteocalcin, which influences blood sugar regulation, fat deposition, and even male fertility. So, as you can see,
human bones
are far more than simple scaffolding; they are multi-functional powerhouses that are intricately linked to virtually every aspect of our health and survival. Keeping your
skeletal system
strong isn’t just about avoiding fractures; it’s about supporting a symphony of life-sustaining processes that make you, well,
you
!\n\n## A Journey Through the Human Skeleton: Major Bone Groups\n\nAlright, let’s take a virtual tour of your amazing internal architecture, exploring the major
human bones
that make up your entire
human skeleton
. Our skeleton is generally divided into two main parts: the
axial skeleton
and the
appendicular skeleton
. Each part has a crucial role, and understanding them helps us appreciate the full scope of our body’s design. First up, we have the
axial skeleton
, which forms the central axis of your body. Think of it as the core framework, providing support and protection for your vital organs. This part includes three main groups: the skull, the vertebral column, and the thoracic cage. The
skull
, guys, is truly a marvel. It’s made up of 22 different bones (cranial and facial bones) that are mostly fused together, creating an impenetrable fortress for your brain. It also houses your sensory organs for sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Without this robust structure, our delicate brains would be incredibly vulnerable. Next, the
vertebral column
, or spine, is your body’s main support structure. It’s composed of 33 irregular bones called vertebrae, stacked one upon another, separated by intervertebral discs that act as shock absorbers. This flexible column protects your spinal cord, allows for a wide range of movement – bending, twisting, arching – and supports the weight of your head and trunk. From the cervical vertebrae in your neck to the lumbar vertebrae in your lower back and ending with the fused sacrum and coccyx, each segment is critical. Then there’s the
thoracic cage
, which consists of your sternum (breastbone) and 12 pairs of ribs. This protective cage encapsulates your heart and lungs, vital organs that need constant safeguarding. The ribs are curved bones that articulate with your thoracic vertebrae, providing both protection and flexibility for breathing. Without the
axial skeleton
, we’d simply be a formless mass. Now, let’s move to the
appendicular skeleton
. This part comprises the bones of your limbs (arms and legs) and the girdles (pectoral and pelvic) that attach them to the axial skeleton. These are the bones that enable all your amazing movements and interactions with the world. The
pectoral girdle
, made up of your scapulae (shoulder blades) and clavicles (collarbones), connects your upper limbs to the axial skeleton, allowing for incredible flexibility and range of motion in your arms. Your upper limbs themselves consist of the humerus (upper arm bone), radius and ulna (forearm bones), and the many small bones of your wrists (carpals) and hands (metacarpals and phalanges). These
human bones
allow you to manipulate objects, write, eat, and express yourself through gestures. Down below, we have the
pelvic girdle
, formed by the two hip bones (ossa coxae), which connect your lower limbs to the axial skeleton. This strong, basin-shaped structure provides robust support for your trunk, protects your pelvic organs, and is critical for transmitting weight from the upper body to the legs. Finally, your lower limbs include the femur (thigh bone – the longest and strongest bone in your body!), the patella (kneecap), the tibia and fibula (shin bones), and the bones of your ankles (tarsals) and feet (metatarsals and phalanges). These bones are engineered for weight-bearing and locomotion, allowing you to stand, walk, run, and jump. Understanding how these two major divisions of the
human skeleton
work together gives us a profound appreciation for the intricate and highly functional design of our own bodies, truly making our
body’s foundation
a masterpiece of natural engineering. Each bone, no matter how small, plays a specific and crucial role in this complex system, demonstrating the unparalleled wisdom of your own anatomy.\n\n## Keeping Your Bones Strong and Healthy: Tips for a Lifetime\n\nKeeping your
human bones
strong and healthy throughout your life, guys, isn’t just a matter of luck; it’s a proactive commitment to your
bone health
that pays dividends in mobility, independence, and overall quality of life. Think of your bones as a bank account for minerals like calcium – you need to make regular deposits to ensure you have enough reserves, especially as you age. One of the most critical aspects is
nutrition
. Your bones absolutely
crave
calcium. Dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese are excellent sources, but if you’re lactose intolerant or vegan, don’t sweat it! Leafy green vegetables such as spinach and kale, fortified plant-based milks, tofu, and certain fish like salmon and sardines are fantastic alternatives. But calcium alone isn’t enough; your body needs Vitamin D to properly absorb calcium from your gut. The best source of Vitamin D is sunlight exposure, as your skin produces it when exposed to UV rays. However, dietary sources like fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified foods (milk, cereal) are also important, and many people benefit from Vitamin D supplements, especially in regions with limited sunlight or for specific dietary needs. Beyond these two superstars, other nutrients like magnesium, Vitamin K, and phosphorus also play supporting roles in maintaining optimal
bone density
and structure. So, a balanced diet rich in whole foods is fundamental. Next up is
exercise
. This isn’t just about building muscle; it’s absolutely vital for stimulating bone growth and density.
Weight-bearing exercises
are particularly effective because they put stress on your bones, signaling them to become stronger. Activities like walking, jogging, hiking, dancing, and playing sports are excellent examples. Even strength training with weights or resistance bands helps, as the pulling and pushing action of muscles on bones also encourages bone formation. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity weight-bearing exercise most days of the week. Remember, bones respond to stress by becoming denser, so a sedentary lifestyle is one of your bones’ biggest enemies. Avoiding harmful habits is equally important for preserving your
bone health
. Smoking, for instance, significantly reduces bone density and increases fracture risk. Excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with calcium absorption and bone formation, while also increasing your risk of falls. Being mindful of these lifestyle choices can have a profound impact on the longevity and strength of your
skeletal system
. And finally, don’t forget
regular check-ups
. As you get older, especially for women post-menopause and men over 70, discussing bone density screenings (like DEXA scans) with your doctor is a smart move. Early detection of conditions like osteopenia or osteoporosis allows for timely interventions, whether through diet, exercise, or medication. Building and maintaining strong
human bones
is a lifelong endeavor, but by making informed choices about your diet, staying active, and avoiding detrimental habits, you’re investing in a future of robust health and unhindered movement. Your body – and especially your incredible
body’s foundation
– will thank you for it!\n\n## The Future of Bone Health and Research\n\nLooking ahead, guys, the future of
human bones
and
bone health
is incredibly exciting, with ongoing
bone research
constantly pushing the boundaries of what we understand and how we can treat various bone-related conditions. While we already have a solid grasp on maintaining
bone density
through diet and exercise, scientists are delving deeper into the molecular mechanisms of bone formation and repair, promising even more innovative solutions. One major area of focus is
bone regeneration
. Imagine a future where severe bone fractures or defects from disease aren’t just mended with metal plates, but where the body can regrow its own functional bone tissue efficiently. Researchers are exploring advanced biomaterials, stem cell therapies, and growth factor delivery systems to encourage native bone regeneration. This could revolutionize treatments for complex fractures, non-union breaks, and even bone loss due to cancer or trauma, essentially giving your
skeletal system
a supercharged repair kit. Another significant battle is against osteoporosis, a debilitating condition where bones become brittle and fragile. While current
osteoporosis treatment
options exist, including bisphosphonates and hormone therapies, ongoing research is targeting new pathways to prevent bone loss and even stimulate new bone formation more effectively, with fewer side effects. This includes novel drug targets that influence osteoclast and osteoblast activity, as well as personalized medicine approaches based on an individual’s genetic profile and risk factors. The goal is to make osteoporosis a manageable condition, if not entirely preventable, ensuring that more people can maintain strong
human bones
well into old age. Furthermore, advancements in diagnostic imaging are allowing for earlier and more precise detection of bone issues. High-resolution imaging techniques can identify subtle changes in bone structure long before a fracture occurs, enabling proactive interventions. Wearable technology and AI are also starting to play a role, monitoring activity levels and even predicting fracture risk based on gait analysis and other physiological data. This integration of technology with biology promises a more personalized and predictive approach to
bone health
. We’re also seeing increasing interest in the connection between bone health and other systemic conditions. For example, the role of osteocalcin and other bone-derived hormones in metabolic health, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease is an active area of investigation. This holistic view emphasizes that our
human bones
are not isolated structures but integral components of a complex, interconnected biological system. The potential for breakthroughs in targeted drug delivery, gene therapy for genetic bone disorders, and even custom 3D-printed bone implants is vast. These developments highlight a future where maintaining a robust
body’s foundation
becomes even more attainable, pushing us closer to a world where strong, healthy
human bones
are a given, enabling a higher quality of life for everyone. It’s a testament to human ingenuity constantly striving to enhance and preserve the incredible engineering within us.

